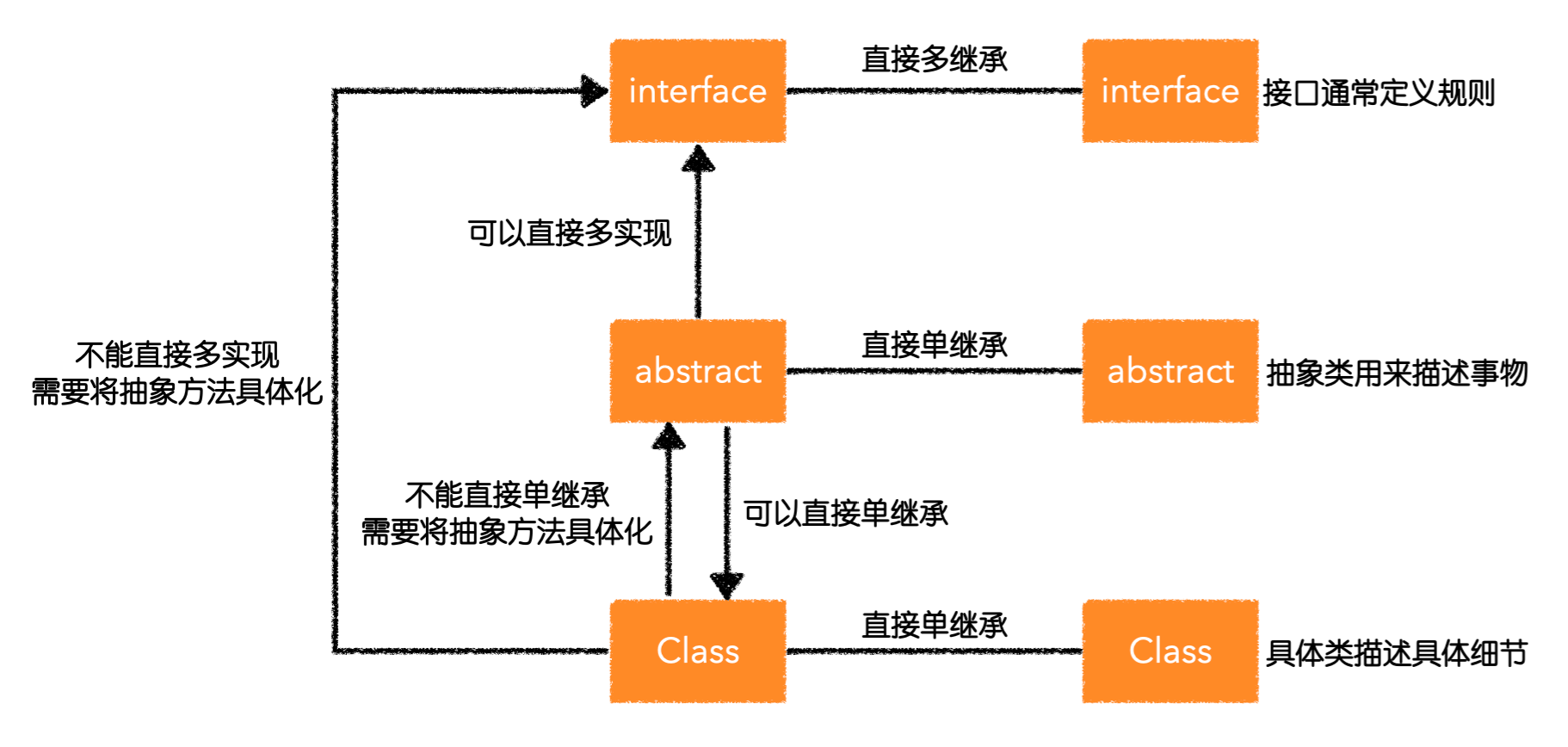
接口
接口通常是用来定义规则的。接口是抽象类的极致,不能有非抽象方法。
接口的结构与类相似,只是将 class 关键字 替换成 interface 关键字。
成员特点
接口的成员与类的成员不同,接口成员的特性如下:
- 接口的属性默认且只能是公有的静态的常量(即 public static final)
- 接口的方法默认且只能是公有的抽象的(即 public abstract)
- 接口没有程序块
- 接口没有构造方法
接口的实现
因为没有构造方法,因此接口是无法创建对象的。
接口只能通过子类多实现(implements)来做事。
子类实现接口的格式:...implements 接口名称[, 其他接口名称, 其他接口名称..., ...]
java
public interface Animal1 {
void eat();
void sleep();
}
public interface Animal2 {
int Age = 1;
void growUp(int year);
int getAge();
}
public class Person implements Animal1, Animal2{
private int Age = 1;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("I am eating");
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("I am sleeping");
}
public void growUp(int year) {
Age += year;
}
public int getAge() {
return Age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.eat();
p.sleep();
p.growUp(9);
System.out.println("I am " + p.getAge() + " years old now.");
}
}与其他类的关系
接口不能继承别的类,接口是最抽象的。
- 抽象类可以直接多实现接口
- 具体类不能直接多实现接口,需要将接口中的抽象方法实现出来
- 接口之间是可以直接多继承的